Have you ever been too drunk to drive back home after a fun night out? Or has your car broken down when you were in a rush to reach work or catch a flight? Well, if you have, then you know that in such situations, the Uber mobile app is your knight in shining armour. Call a ride with a tap on your smartphone screen and travel to wherever you have to.
The convenience and easy accessibility that Uber offers and the uniqueness of the Uber business model have helped it grow like wildfire globally. Apps like Uber have become especially popular among the large segment of population worldwide that does not own cars, and residents of large cosmopolitan cities who face issues of traffic and parking – for them, Uber is a smart solution for their everyday commuting needs.
With time and the rising popularity of Uber and similar ride-hailing services, a growing number of tech investors and innovators are looking to tap into this market. People interested in developing an app like Uber wonder, “What is Uber’s business model?”, “How does Uber make money?”, “What technology does Uber rely on?” and other similar questions. If you share the same concerns, do read on! Today, we bring you the answers to all your questions.
What Is Uber?
Unless you have been living under a rock, you probably know about ride-hailing services like Uber and have a general idea of how Uber works. Uber was founded as UberCabs in March 2009. It went live for the first time in July 2010 in San Francisco, making it a first-of-its-kind technology to connect drivers and riders in demand. Uber is not a traditional taxi service because it does not own vehicles or employ drivers. It simply offers the service of developing technology that connects the drivers with the riders. This is the basic framework on which other Uber like apps work as well.
Since 2009, Uber’s business, customer base, and network of drivers has grown exponentially, and so has the competition. Even with increasing competition (owing to the launch of other apps like Uber, such as Lyft, Ola, DiDi, and Taxify), Uber undeniably leads the ridesharing industry. As of November 2019, Uber held around 70% of the market share of the leading ride-hailing companies in the United States, followed by Lyft with a 29.2% market share.
Uber’s success is a result of the unique business model of Uber and the robust technology that powers Uber’s platform. Before we get into the discussion about what Uber’s business model is and what technology it relies on, let’s look at some quick facts about Uber.
Quick Facts About Uber
- Founders: Travis Kalanick and Garrett Camp
- Company Headquarters: San Francisco, California, United States
- Funding received by Uber: $24.7 Billion (as of April 2019)
- Revenue: 3.166 billion USD (as of June 2019)
- Number of Active Users: 91 million consumers per month and 3.9 million drivers (as of December 2018)
- The average number of daily Uber Trips: 14 million trips completed each day (as of December 2018)
- Global Operations: Uber operates in 63 countries and mobilizes more than 700 cities globally.
Uber’s App Overview
Uber’s app, like many other smartphone apps, is a cross-platform application. This means that it built to work on different devices and operating systems, like iOS and Android. Uber’s app for iOS and Android can be downloaded from their respective app marketplaces. The app is the main Uber platform where the riders and drivers log on to avail and provide the service. The nature of Uber’s business is very app-centric. Therefore, Uber has designed a user-friendly app with features like gamification to ensure Uber users can easily use it.
How Uber Works for Drivers and Riders
Uber’s platform is a two-sided marketplace (we will discuss this in detail later in the article), which means it needs to work perfectly on both sides. For this, Uber has developed two applications – rider-side and driver-side – to make it easier for both parties to connect with each other.


How the Uber Business Model and App Work Together
Step 1 – Profile Registration
Profile registration is the first step of using Uber. Every Uber app requires a valid profile registered against a valid cellphone number and an email address. It means every user (driver or passenger) needs to set up a profile before they can start using Uber’s services.
The process of profile registration and login for the passenger-side app requires functionalities such as email and/or social media log-in, debit and credit card details, and payment method selection. The process for profile registration is more complex for the driver-side app as it consists of additional functionalities such as tax number verification, administrator approval, schedule of driving hours, etc.
Step 2 – Request a Cab
When a rider first opens their app, it automatically shows their present location on the map. When a destination location is entered into the ‘Where to’ box, it updates to show a route of the present location to the destination on the map. Uber’s ride calculator automatically loads the relevant information about the trip, such as different vehicle options, the fare estimates for each option, and the estimated time of drop-off. The user needs to choose a vehicle option and drag the pin on the map to set the exact pickup location. Once this step is completed, Uber proceeds to the next step of the process.
Step 3 – Matching
When a ride request is made by a user, Uber notifies the available drivers in the nearby area. The notification pops up on the drivers’ apps and they may choose to accept or reject the rider’s request. If a rider is successfully matched with a driver, they are notified about it. They can then view the booking details such as the type and make of the vehicle, the name and contact number of the driver, and how far the driver is from the pickup location. The map on the rider’s app shows the vehicle’s movement and is automatically notified when the driver’s vehicle is a minute away.
Step 4 – Ride
After the verification of the booking details between the rider and the driver, the ride can be initiated. Throughout the trip, the rider and driver can see their movement on their respective apps if they are connected to the Internet. The driver-side app also gives the option to access turn-by-turn navigation.
Step 5 – Payment and Rating
When the ride ends, Uber notifies both the rider and the driver about the fare for the trip, which can be paid by the rider through their pre-selected method of payment. Riders and drivers can also rate each other from 1 to 5 stars based on their experience after every ride. Additionally, riders can tip the driver and leave them compliments within the app.
How Does Uber Make Money – Uber Business Model Explained
At the helm of the successful business model of uber are various factors such as their pricing policy, marketplace framework, and affiliated services. These work in conjunction to help Uber make money and contribute to the success of Uber’s business.
Uber’s Framework
The business model of Uber follows a framework known as a two-sided marketplace, a concept that became popular with the boost in technological advancement. A two-sided marketplace is a platform that connects two ends of a transaction. In Uber’s case, they are the drivers and the riders. In other words, Uber is only a platform that is developed with the right set of functionalities and a user-friendly interface to help connect drivers and passengers. Uber does not own any of the vehicles, nor does it employ any of the drivers. It only makes money by facilitating transactions between both parties. This means Uber makes money on both sides by charging a fixed amount of fee for every vehicle registration and getting a small share of every ride’s fare. Other similar Uber like apps also function the same way.
On one hand, Uber is able to attract drivers because of the flexible work schedules, an extra source of income, and easy registration and payment procedures. On the other hand, Uber draws customers by offering affordable commuting options, minimum waiting time, door-to-door pickup and drop-off, and a safe, high-quality service owing to Uber’s 24/7 customer support and review and rating system.
Uber’s Revenue Generation Model
Like every other business, sources of revenue are essential for the Uber business model as well. The revenue generation model of Uber comprises profitable pricing strategies, a multitude of car service categories, and subsidiary offerings that contribute to Uber’s revenue stream.
Surge Pricing
Uber’s most profitable revenue strategy is its surge pricing model, where Uber sets the ride fares based on the situation at that point in time. It works on the rudimentary principle of demand and supply. If the demand for rides increases but there is only a small number of drivers to cater to it, then the price per kilometre increases. In such a situation, the price would depend on a number of factors including the total number of ride requests and the number of available drivers in a given area. Depending on this, ride fares can be anywhere between 1.5 times or sometimes even 4 times the original fare amount. This is essentially what surge pricing is, and it is a key element of Uber’s business model.

Surge pricing applies automatically when there is a demand-supply imbalance, especially in times of rush hour, special public events, and severe weather conditions. In the past, Uber has received criticism from users for overcharging for rides. However, Uber defends the surge pricing policy as a way to attract more drivers and encourage them to head to the area with higher demand, this helps restore the demand-supply balance over time and maintain reliability.
Multiple Car Categories
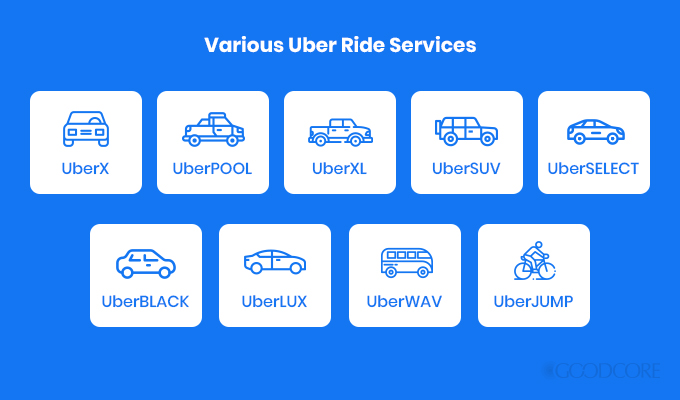
Unlike other Uber like Apps, Uber’s revenue generation model is unique because of its wide variety of offerings. Uber was initially launched solely as a cab service in 2009 but over the last decade, Uber has expanded its offerings to include multiple car categories for their cab service. Originally, Uber only offered UberX – a regular 4-door car to carry up to 4 passengers – but over time, Uber introduced new car categories, each at a different price point, to target a wide range of customer segments. These include:
- UberXL – a cost-efficient category of larger 4-door vehicles that can carry 6+ people
- UberPool – an environmentally-friendly carpooling option for 4 or more passengers headed towards the same destination
- UberSUV – a special category for SUVs only
- UberBlack – a premium category with only black luxury cars for those who travel in black cars
- UberLUX – a high-cost category with professionally driven luxurious cars
- UberWAV – a service for wheelchair users with wheelchair accessible vehicles
- UberJUMP – a service to rent and use electric bikes and scooters
With increasing global reach, Uber also offers other kinds of categories for different cities. For instance, UberMoto offers affordable motorcycle rides and UberAuto is an option for auto rickshaw rides that are offered in different cities in the Asian region.
Other Services
Over the course of their operation, they have also expanded the business model of Uber by branching out to offer services other than ride-hailing. These include:
- UberEats – Debuted in major cities in the USA in 2015 for on-demand food delivery services
- Uber Freight – A service for shipping and carriers which was first launched in 2017
- UberAir – To be introduced in 2023 for shared air transportation between cities

Although these services are fairly recent, their popularity among Uber users has made them an important part of Uber’s business model.
What Technologies Does the Uber Business Model Rely On?
Anyone interested in creating an app like Uber is always curious about what technologies Uber’s business model relies on. Here is the answer.
Uber relies on solid technology that has allowed Uber’s business model to sustain and grow progressively over the years. Obviously, Uber’s app is what makes it possible for the business to function, and their app-centric business operation means Uber’s main focus is on making sure their app functions flawlessly. Uber has consistently rolled out updated and advanced versions of their mobile application to keep up with the recent technological advancements. These include adding newer features and functionalities to ensure better performance, higher security, and efficient service.
Geolocation
Geolocation and mapping are the most important components of a technology stack for a ride-hailing app like Uber. It is a core functionality for location detection that works behind the scenes to allow the app to get the precise locations of drivers and passengers, calculate the distance, suggest routes, and track the ride. Uber’s routing technology works constantly from the moment users launch the app until the end of their rides.
Geolocation works slightly differently for the iOS and Android versions of Uber’s app. The Android app uses Google Location APIs that make it possible to determine the precise location of a user’s device and displays it on the map integrated within Uber’s application. On the other hand, the iOS version relies on the CoreLocation framework to obtain the location of a device, and the MapKit framework to provide driving directions and determine routes.
Uber has constantly worked to make their geolocation and mapping technology smarter and more efficient to maintain their position as the market leaders of the ride-hailing industry.
Messaging and Push Notifications
Messaging and push notifications are basic features that make the process of requesting an Uber ride convenient for users. When a ride request is made through Uber’s app, it sends out a couple of push notifications and text messages to keep the user updated about their request.
Push notifications are sent when a driver accepts your request and when the driver gets close to or arrives at the pickup location. Users are notified in instances of ride cancellations as well. Uber even introduced a notification feature to let users know when the surge pricing multiplier is turned off. If a device has push notifications disabled or if it is in offline mode, then text messages are sent to notify users. For that, Uber relies on Twilio, a telecommunication provider.
Uber recently rolled out their inter-app communication features that allow a rider’s app to connect with the driver’s app through real-time messaging. This built-in messaging technology is an important feature of Uber’s app that allows easy and quick communication between drivers and passengers.
Payment Integration
Uber offers both cash and cashless payment methods for users to pay ride fares. A user can either pay in cash at the end of the ride or make a payment through their debit or credit card. Hence, Uber’s app relies on integration with payment gateways and tools to make the payment process smooth and fault-free.
For payment through debit and credit cards, Uber needs to assure compliance with certain security standards, e.g. the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) in the United States. To easily and securely process payments, Uber uses Braintree Payments, a technology that is integrated into Uber to process all kinds of card payments internationally and in the US. Braintree also allows Uber users to make payments using their local currency. This has been monumental in helping Uber expand its services to 700+ cities worldwide.
For further ease of payment, Uber also relies on PayPal integration which gives users the option to make payments directly from their PayPal accounts within the app. Uber also implements PayPal’s Card.io for the iOS version of their application for the purpose of credit card scanning using your smartphone’s camera.
Wrapping Up the Uber Business Model
Uber and similar ride-hailing services are not just examples of profitable business models. They are also smart solutions that are providing convenience to people by making their daily commute easy for them. This is especially favourable for people living in large cosmopolitan cities with traffic issues and lack of parking, and for people living in developing countries who do not have a proper public transport system. Moreover, the newly-introduced offerings such as JUMP and UberPool are also of interest to people who are looking for environmentally friendly ways of commute.
Overall, the future of the ride-hailing industry looks bright and full of potential for further innovation. If you are interested in investing in Uber like apps, you require two things: thorough knowledge of the business model of Uber and similar ride-hailing services (which I hope we have provided you in this article) and the services of a top-notch mobile app development company.