As a software development company, this is a question we get asked a lot. The truth is, there isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer. The cost depends on many factors, such as the complexity of features, the design requirements, the technology stack, and whether you hire freelancers, an in-house team, or a custom software development company.
Understanding these cost drivers can help you plan realistically, avoid surprises, and make smarter investment decisions.
In this post, we’ll break down the main factors that influence web app development costs, typical pricing ranges, and tips for getting the most value from your budget, so you can confidently move forward with your project.
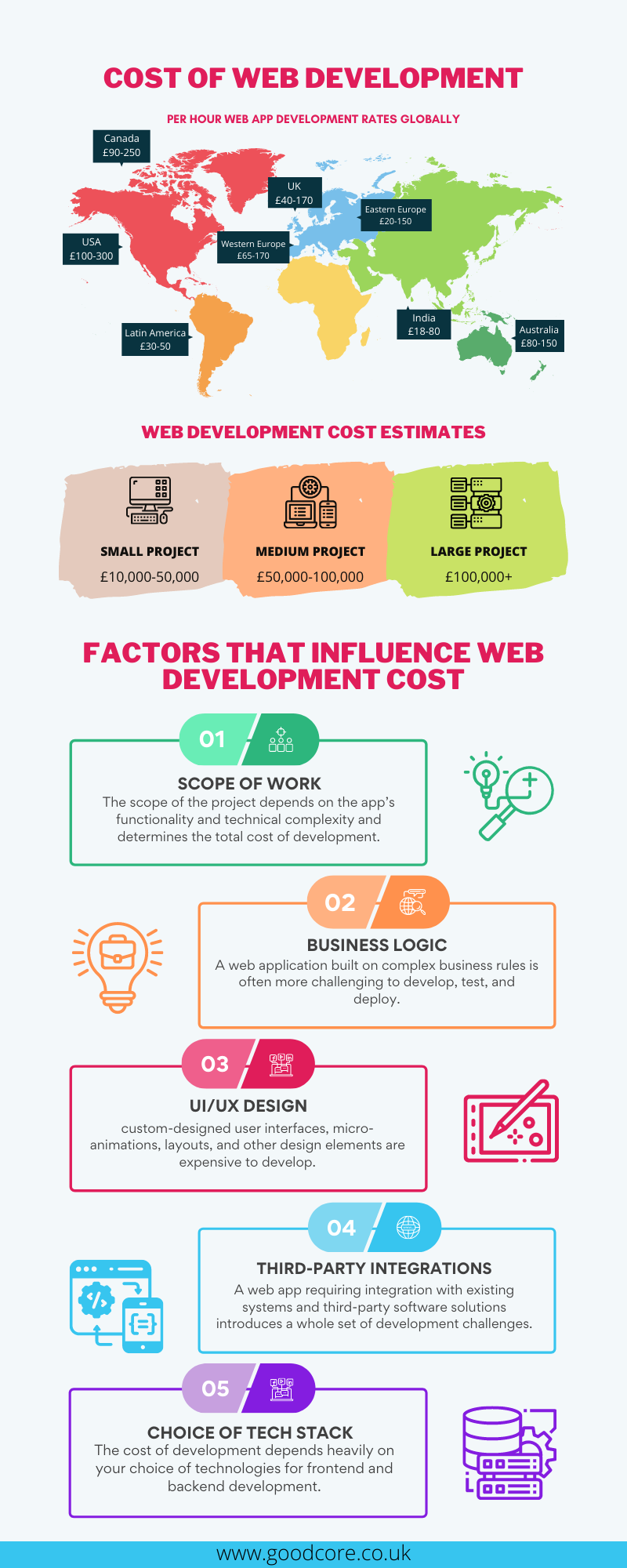
Factors Influencing Web Application Development Cost
Before we dive into cost ranges, it is important to understand what drives web app development costs. Here are the six most influential factors:
-
Scope of Work & Complexity

The scope of your project plays a huge role in determining costs. A simple content-based application will naturally be less expensive than an enterprise-grade app with complex workflows, infrastructure, and automation. The more screens, features, and modules your app requires, the higher the overall development cost will be.
-
Business Logic
Business logic refers to the set of rules, processes, and calculations that define how your application actually works behind the scenes to meet your business goals. It’s the “brain” of the app that decides what happens when a user takes an action.
The more advanced the business logic and calculations involved, the more costly the app will be. For example, a web-based financial trading platform costs significantly more than a basic booking system because of the advanced ‘business logic’ and calculations involved.
-
UI/UX Design
Design also impacts cost. A web app with custom animations, advanced interactions, and unique layouts requires more design and development hours. Using standardized templates can save costs, but this often comes at the expense of having to compromise on the quality of the user experience.
-
Third-Party Integrations
Integrating your app with external systems such as payment gateways, CRMs, ERPs, or analytics tools requires configuration, security considerations, and thorough testing, which in turn increases costs.
-
Choice of Technology Stack
Your technology stack (front-end, back-end, and database) directly affects both development speed and pricing. Popular JavaScript frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue are widely adopted, which makes it easier and often more affordable to find developers. Hence, the choice of back-end and database technologies also plays into scalability and overall cost.
Also Read: Front-end Technologies
-
Vendor Location & Pricing Model
The vendor (development partner that you are outsourcing for the project) Where your vendor is located has a major impact on the overall costs, as rates differ across continents, from the UK to Eastern Europe, and Asia. Furthermore, the pricing model you choose, whether fixed-price, time-and-materials, or a dedicated team, also influences the final project figure.
Learn more about how web applications are developed in our detailed web application development guide.
How Much Does App Development Cost?
To make costs easier to understand, we have broken them down by development phases. A traditional web app development process involves seven main stages. Let’s take a look at how much investment would be required for each phase.
1. Discovery & Planning
What happens: Requirement gathering, market research, feasibility study, and technical documentation.
Why it matters: One of the most important stages, where you lay the foundation, make a roadmap, define roles and set KPIs, so you can easily track how smoothly/successful the project is going/has turned out to be.
Estimated cost: £3,000 – £10,000
2. UI/UX Design
What happens: Wireframing, prototyping, user interface design, and mapping out user journeys.
Why it matters: A clean, intuitive design will boost user satisfaction, improve engagement, and lower the risk of churn (the rate at which users or customers stop using your app or service over a given period of time) by making it easy and enjoyable to use.
Estimated cost: £5,000 – £20,000
3. Front-End Development (User Interface)
What happens: Building the customer-facing side of the app, including features like dashboards, forms, animations, and everything the user directly interacts with.
Why it matters: This is the stage where your app’s design turns into something users can actually click, scroll, and interact with. A smooth, responsive front-end makes the app feel fast and easy to use, keeping users happy and encouraging them to come back.
Estimated cost: £8,000 – £40,000
4. Back-End Development (Business Logic, APIs, Databases)
What happens: Setting up databases and APIs that power the app behind the scenes. This is where the business logic comes in, where you define the rules and workflows to make your app function.
Why it matters: A strong back-end keeps everything running smoothly behind the scenes. It makes sure that your app can scale with more users, stay secure, and perform reliably, no matter how complex the tasks get.
Estimated cost: £15,000 – £60,000
5. Quality Assurance & Testing
What happens: Running manual and automated tests to check functionality, usability, security, and performance across different devices and browsers.
Why it matters: Thorough testing is required so you can make sure that your app is secure, running smoothly, and delivers a seamless experience to users before it can be launched in the market.
Estimated cost: £5,000 – £20,000
6. Launch
What happens: Configuring servers, setting up hosting, preparing CI/CD pipelines, and releasing the app to a production environment.
Why it matters: At this stage, you are releasing your app into the market, which will be used by real users. It is important because a smooth release process minimizes downtime and avoids costly launch-day issues.
Estimated cost: £2,000 – £8,000
7. Maintenance & Updates
What happens: Ongoing bug fixes, performance monitoring, system updates, and adding new features as user needs evolve.
Why it matters: After launching, it is necessary to keep the app maintained regularly and update it with new features, so it remains secure, relevant, and competitive over time, ensuring long-term success.
Estimated cost: 15 – 20% of the original development cost (annually).
In-House vs. Outsourced Development Cost Comparison
Building a web app can be approached in two main ways: keeping everything in-house or partnering with an external development team. Each option comes with its own cost structure, advantages, and challenges, as listed below.
In-House Development
- Pros: Full control, team alignment, faster communication.
- Cons: High overhead (salaries, benefits, recruitment costs, training, tools).
- Cost: Maintaining an internal development team in the UK can easily exceed £250,000 annually.
Outsourced Development
- Pros: Access to specialised talent, flexibility, lower upfront investment, faster time-to-market.
- Cons: Requires vendor due diligence and clear communication.
- Cost: A project-based outsourcing model can range from anywhere between £10,000 and £100,000+, depending on the complexity of the project and other factors (as mentioned above).
If you are looking to outsource a vendor in the UK, check out our blog on top web development companies in the UK.
Impact of Technology Stack on Web App Cost
The technology stack is basically the toolkit of frameworks, programming languages, and services that your app is built on. Choosing the right mix can save you money and headaches in the long run, while the wrong choice can make your app harder to scale, maintain, or even hire developers for.
There are four types of technology stacks. These are:
Front-End Frameworks
Popular options include React, Angular, and Vue. React is often the most cost-effective because it has a massive community and talent pool, making it easier (and cheaper) to find skilled developers. Angular and Vue are also powerful, but depending on your project needs, they might be slightly more expensive or harder to hire for.
Back-End Technologies
Options include Node.js, .NET, PHP, Java, and Python. Each comes with its own licensing rules, hosting requirements, and developer availability. For example, Node.js can be a great fit for fast, scalable apps, while .NET might be better for big-scale applications but could cost more in licensing.
Databases
Every app needs a place to store data. The choice often comes down to SQL (structured databases) versus NoSQL (more flexible databases). SQL can be cheaper for simpler apps, while NoSQL might be better if you’re dealing with large amounts of unstructured data or need to scale quickly.
Cloud Services
Hosting your app on platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud is common today, but each provider has different pricing models. Some charge more for storage, others for data transfer.
Also read: best IDE for web development
Front-End vs. Back-End Development Costs
When budgeting for a web app, it helps to understand how costs are typically divided between the front-end, back-end, and integration layers.
While we have already touched on what these layers involve (and how much they cost), here we will focus on how much of your budget each one usually takes up, and how that balance can shift depending on the type of app you are building.
Front-End
It often takes up around 20 – 30% of the total budget. The cost mainly depends on how engaging you want the interface to be. Using standard templates can reduce costs, while custom animations, interactive dashboards, or highly unique designs will push them higher.
Back-End
This usually makes up 30 – 50% of the budget. Apps that handle a lot of transactions, complex workflows, or sensitive data (like finance or healthcare apps) typically require more back-end technology investment.
Integration Layer
Standing in between front-end and back-end, this layer ensures everything links to each other smoothly. While it is not always the biggest cost driver, complex third-party integrations, like payment gateways, CRMs, or analytics tools, can increase overall costs.
For example:
- A data-heavy web app like an analytics dashboard will likely spend more on back-end development,
- While an e-commerce platform may need to balance costs evenly between front-end (for a smooth shopping experience) and back-end (for inventory, payments, and logistics).
Ongoing Maintenance and Support Costs
Many businesses underestimate post-launch expenses. After deployment, you will need to set aside a budget for:
- Bug fixes & security patches
- Infrastructure scaling
- Feature upgrades
- Compliance updates (e.g., GDPR)
Minimum Viable Product (MVP) Cost Estimation
If you are a startup or just beginning to build an app, the first step should be to create a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). An MVP includes only the core features your users truly need, like sign-up and basic workflows.
For example, an MVP for a food delivery app might only let users create an account, browse restaurants, place an order, and make a payment, without extra features like loyalty programs or advanced filters.
The idea is to keep it simple so you can launch faster, and it usually falls within a cost range of £10,000 – £25,000. This approach helps you get your product in front of actual users quickly, gather feedback, and validate your idea with investors before spending heavily on a full-scale solution.
Cost Forecasting and Project Estimation Tools
Planning and forecasting costs can save you from budget overruns. Here are some useful tools and methods for estimating costs:
- Agile Estimation: Breaks down features into story points for better forecasting.
- Planning Poker: Collaborative estimation technique used by Agile teams.
- Cost Calculators: Many firms offer online cost calculators.
- Consultations: Sessions with software development companies to get one-on-one discussions on tailored projects and get cost estimates.
Final Thoughts
Developing a web application requires significant investment, but it can bring immense returns if done strategically. By making informed choices at every stage, you can control expenses without compromising on quality.
At GoodCore, we have been helping businesses build custom web applications for over 16 years. Whether you’re planning a startup MVP or a large-scale enterprise solution, our team can guide you through every step, from cost forecasting to final deployment.
FAQs
What is the average cost of web app development?
Web development prices are directly related to the complexity of the application and the time, skills, and expertise required to build it. It also depends on your choice of engagement model and the location of the vendor.
On average, the total costs of app development can fall anywhere between £10,000 and £100,000 or more depending on these factors.
Can I build an app for less than £50,000?
App development costs are subjective to a number of factors such as the requirement of the application, complexity, technologies, and the pricing model. However, it is possible to create an app that is simple to moderately complex for less than £50,000. If you want to strictly stick to a budget of £50,000, you can choose a vendor that offers a fixed-scope, fixed-price model.
How long does it take to develop a web application?
The development varies from project to project depending on the scope of work, technical complexity, and size of the team. A simple web application like landing pages can be developed within a month or less. While a full-scale complex application that requires features like push notifications and payment integration can take several months to build.





